Essential strategies for Safe and Fast Public Wi-Fi Usage
Connecting to Wi-Fi networks outside your home or workplace has become a daily routine for millions worldwide. Whether you’re at a bustling coffee shop, an airport lounge, or a city park, free internet access is often just a few clicks away-sometimes requiring only an email address to get started. This convenience supports everything from remote work to streaming your favorite shows on the move.
Despite its accessibility, public Wi-Fi differs greatly from private networks in terms of security risks and connection quality. To navigate these challenges effectively, it’s crucial to understand how to enhance your online experience while protecting sensitive facts.
Boosting Your Internet Speed on Shared Networks
Your ability to influence the speed of public Wi-Fi is limited as you don’t control the network hardware or traffic load. Though, several practical measures can definitely help maximize performance:
- Close unnecessary applications and browser tabs that consume bandwidth;
- Pause automatic syncing services like cloud backups temporarily;
- Position yourself closer to routers or access points within venues such as coworking spaces or libraries;
- Select less crowded networks when multiple options are available.
If possible, using a wired Ethernet connection can dramatically improve stability and speed compared with wireless links. Many modern hotels and shared offices offer Ethernet ports; carrying a compact USB-to-Ethernet adapter can be invaluable for frequent travelers relying on dependable connections.
The Vital Importance of VPNs When Using Public Wi-Fi
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) stands out as one of the most effective defenses against cyber threats encountered on open wireless networks. While many use VPNs primarily for bypassing geo-restrictions or masking browsing habits from advertisers, their core advantage here lies in encryption: creating an encrypted tunnel that safeguards your data from other users sharing the same hotspot.
This secure channel prevents hackers from intercepting confidential details such as login credentials or private messages-a critical protection given that cyberattacks targeting public hotspots surged by more than 30% globally over recent years according to cybersecurity reports.
Tactics for Managing Email Addresses When Accessing free Wi-Fi
Many free public hotspots require users to submit an email address before granting access-a practice often leading to inboxes flooded with unsolicited marketing emails afterward. To maintain privacy without losing connectivity:
- Create temporary email accounts via services designed specifically for short-term use;
- Utilize alias features offered by major providers-as an example, Gmail allows adding “+tags” after usernames (e.g., john.smith+wifi@gmail.com), which helps filter incoming mail efficiently;
- email platforms like Outlook provide disposable aliases that can be deleted once spam becomes overwhelming.
This approach keeps promotional clutter seperate from crucial communications while ensuring seamless sign-in during brief sessions on public networks.
Cautious Handling of Saved Networks and Auto-Connect Settings
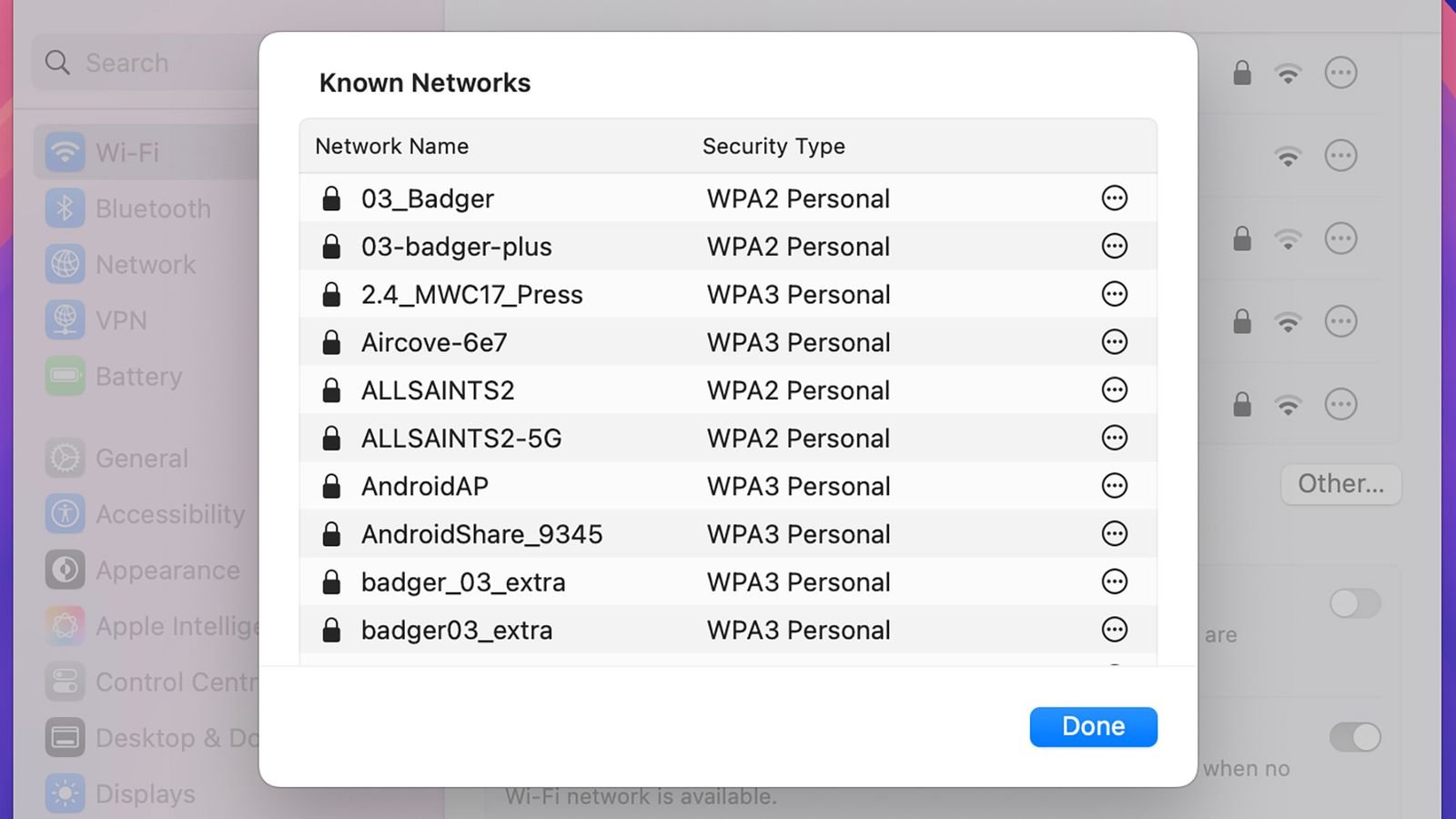
Avoid remaining connected unintentionally by manually disconnecting after finishing usage at any hotspot-and turn off automatic reconnection settings across all devices whenever feasible. Both Windows (Settings > Network & Internet > WiFi > Manage known networks) and macOS (System Settings > Wi-Fi > Advanced…) allow users easy access to view saved hotspots so they can remove outdated or insecure entries promptly.
The Safer Alternative: Using Mobile Hotspots Rather of public Wireless Access Points
If concerns about security outweigh convenience when connecting through unknown wireless sources, consider tethering via your smartphone’s mobile hotspot feature instead:
- Android:
Settings > Network & Internet > Hotspot & tethering - iPhone:
Settings > Personal Hotspot
This method routes traffic through cellular data rather than shared local infrastructure-considerably reducing exposure risks associated with open signals-but keep in mind it consumes mobile data quickly and drains battery life faster than typical usage patterns do.
Select Activities Wisely While Connected Over Public Networks
it’s prudent not only to implement technical safeguards but also carefully choose what tasks you perform over unsecured connections. Avoid conducting sensitive operations such as online banking transactions or entering credit card details unless absolutely necessary.
For lower-risk activities like browsing social media feeds, reading news articles, checking emails without confidential attachments-or simply enjoying entertainment-public connections generally pose less threat.
Streaming high-definition video content may strain bandwidth limits common in crowded hotspots causing interruptions-pre-downloading shows using apps’ offline modes guarantees uninterrupted viewing irrespective of connection quality.
Easily Share Your Connection Across Multiple devices When Needed
If juggling multiple gadgets proves inconvenient at busy locations – laptops running Windows enable sharing their active internet link through built-in mobile hotspot functionality found under:
Settings > Network & ; Internet > Mobile hotspot
Mac computers offer similar options via:
System Settings > General > Sharing > Internet Sharing
Note however macOS restricts simultaneous use cases – wired Ethernet-to-WiFi sharing works well whereas pure wireless-to-wireless rebroadcast isn’t natively supported unlike Windows counterparts.
By adopting these complete tactics-from optimizing physical placement for better speeds through vigilant privacy practices-you’ll enjoy safer experiences whenever tapping into the expanding world of accessible public wi-fi globally today.





