India Advances Aadhaar with Innovative App and Offline authentication
Revolutionizing Everyday Digital Identity Verification
India is enhancing the reach of Aadhaar,the worldS largest biometric identity system,by unveiling a new mobile request paired with an offline verification mechanism. This innovation allows users to confirm their identity without needing continuous online access to the central Aadhaar database, sparking important conversations about privacy safeguards, user consent, and data protection.
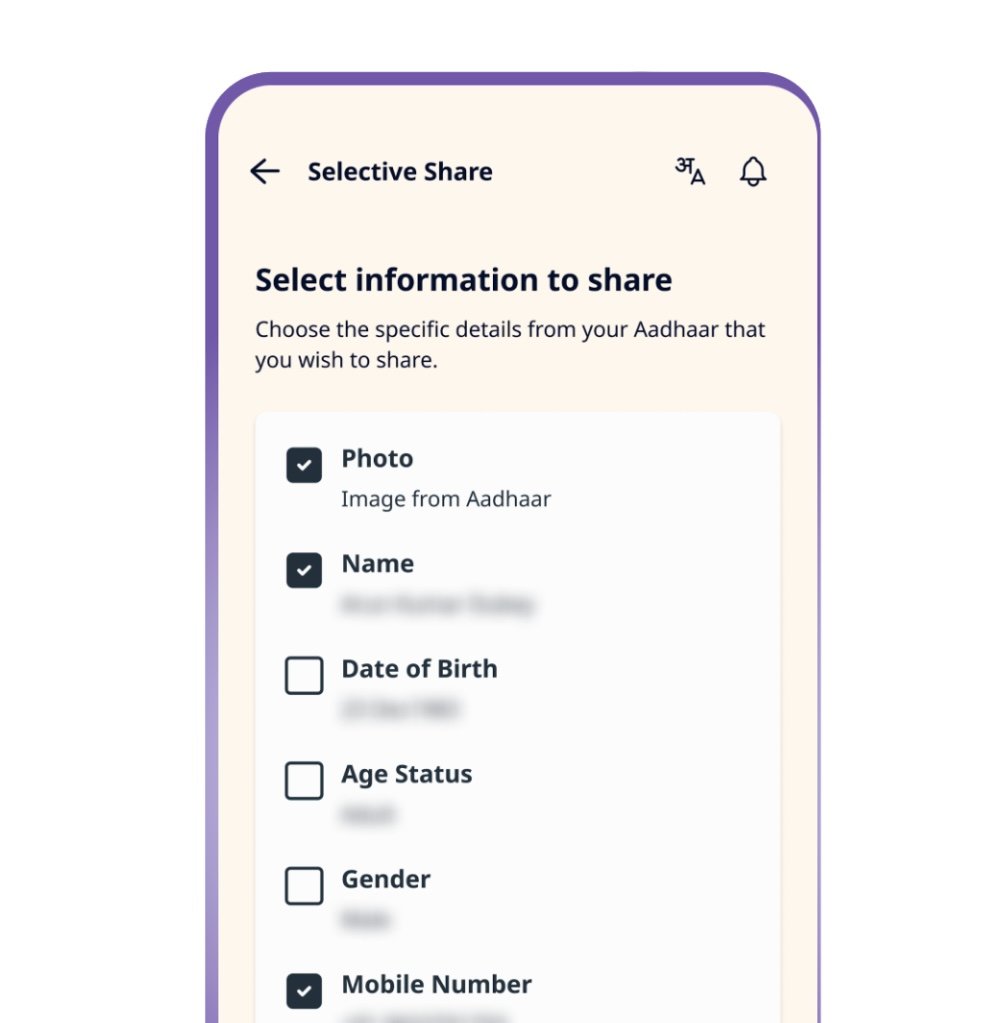
The updated app empowers individuals to selectively disclose specific personal data-as an example, verifying age eligibility without revealing exact birthdates-to various entities such as employers, residential complexes, hotels, and digital payment platforms. Meanwhile, the existing mAadhaar app continues to operate during this transition phase.
Broader Integration into Payment Platforms and Public Services
The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) is actively expanding Aadhaar’s footprint within mobile wallet ecosystems. Google Wallet is set to introduce Aadhaar-based authentication shortly; discussions are underway for Apple wallet integration alongside Samsung Wallet’s current support. These efforts aim to simplify secure identity verification across widely used financial applications.
Source: Google Play
Apart from consumer-facing uses, law enforcement agencies have begun leveraging this technology as well. Such as, Ahmedabad City Crime Branch has integrated offline Aadhaar verification into PATHIK-a hotel guest management system-allowing secure visitor registration without querying the central database repeatedly.
The UIDAI also promotes this new tool as a “digital visiting card,” enabling users to share chosen personal details through QR codes during professional or social interactions-offering a contemporary alternative to conventional business cards while maintaining strict control over shared information.
A Paradigm Shift Toward Consent-Driven Offline Authentication
This initiative reflects Indian authorities’ commitment to replacing outdated methods like photocopying physical IDs or manual document checks with consent-based offline authentication solutions. Officials emphasize that these approaches empower individuals by granting them full control over which aspects of their identity are verified while reducing reliance on constant internet connectivity for sensitive data access.
Tackling Risks Associated With Physical document Handling
A major driver behind promoting offline verification stems from concerns about misuse linked with physical copies or screenshots of Aadhaar credentials-which have often been collected indiscriminately without adequate protections-possibly leading to unauthorized circulation or fraud attempts.
Evolving Regulatory Framework Facilitates Expansion
This rollout aligns with recent regulatory reforms easing restrictions on how public and private organizations can authenticate identities using Aadhaar credentials without direct queries against centralized servers-a move designed both for scalability and enhanced privacy through minimized exposure of personal data during transactions.
User Adoption Skyrockets Amidst Unprecedented Scale
The newly launched Aadhaar app underwent extensive trials before its official release in early 2026. Analytics reveal explosive growth: monthly downloads across all related apps surged from roughly 2 million in October 2025 up close to 9 million by December 2025-rapidly surpassing older versions like mAadhaar within weeks after launch.
This surge builds upon an already massive infrastructure serving india’s population exceeding 1.4 billion people; UIDAI reports issuing more than 1.4 billion unique ID numbers and processing approximately 3 billion authentication requests every month as of mid-2026-highlighting unparalleled scale in global digital identification systems.
The introduction of offline verification complements rather than replaces existing backend frameworks by extending seamless authentication capabilities into everyday citizen interactions spanning sectors such as hospitality services and law enforcement operations.
Navigating Privacy Concerns Amid Rapid Expansion
“The accelerated deployment appears premature given India’s still-developing Data Protection Board framework,” said one expert focused on digital rights advocacy.
“Autonomous oversight combined with broader stakeholder consultation would better safeguard citizen interests.”
Civil liberties advocates warn that despite legal reforms facilitating wider use of biometric IDs like Aadhaar, fundamental vulnerabilities remain unaddressed-including inaccuracies disproportionately affecting marginalized communities; persistent security gaps; limited grievance redress mechanisms; plus risks arising from expanded private-sector involvement prior to comprehensive nationwide data protection legislation taking effect.
Persistent Challenges Effect Vulnerable Groups Disproportionately
An independant audit conducted recently uncovered compliance shortcomings at UIDAI primarily related to protecting user information adequately-raising fears that errors could disenfranchise those most dependent on government-issued IDs for accessing essential welfare programs or financial services inclusion initiatives across rural regions in India today.
Dangers Of Normalizing Private Sector use Without Strong Consent Protocols
Civil society campaigns caution against routine adoption of offline verifications among private entities-including hotels or housing societies-as it risks violating Supreme court rulings limiting non-governmental use of biometric identifiers due precisely to concerns over coercion disguised under voluntary consent.This gradual normalization has been termed “Aadhaar creep,” describing incremental expansion despite judicial restrictions established several years ago.*
The Road Ahead: From Background Utility To Ubiquitous Identity Layer
- Aadhaar is transitioning beyond its initial role as a backend authentication tool toward becoming an omnipresent element embedded deeply within daily social exchanges throughout urban centers nationwide;
- This change draws global attention among governments seeking scalable population-wide ID solutions;
- However it together demands vigilant ethical scrutiny regarding surveillance potential versus individual autonomy;
- User awareness initiatives combined with transparent governance will be vital factors determining weather benefits outweigh risks moving forward;