Soaring Vehicle Costs Expose Deepening Economic Inequality in America
How the Auto Industry Mirrors Economic Divides
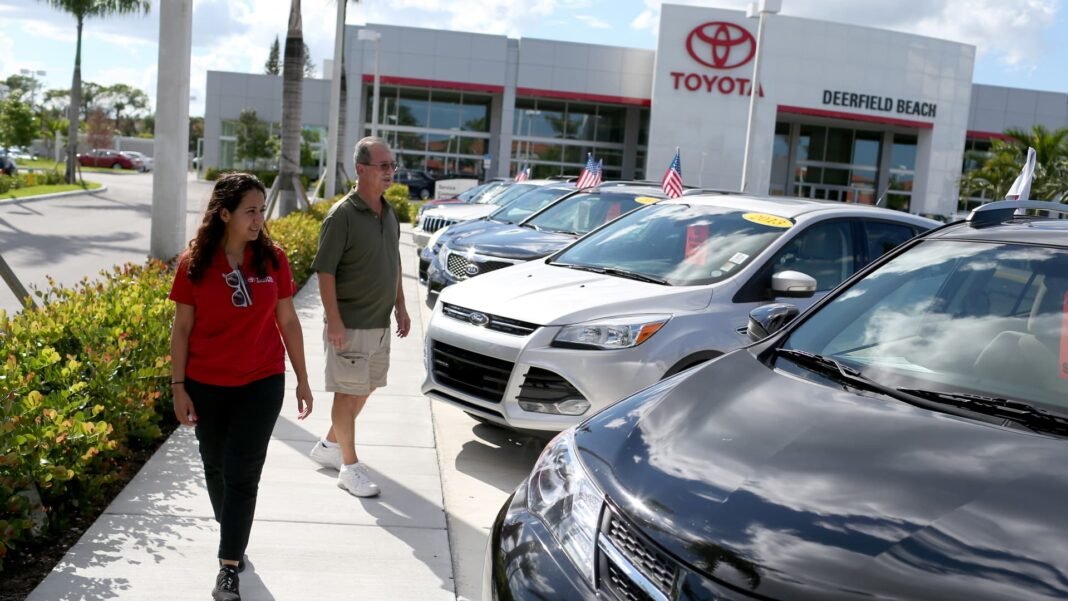
the current state of the automotive market offers a revealing glimpse into the growing financial disparities across the United States. While affluent buyers continue to expand their purchasing power, many lower-income consumers are increasingly sidelined. recent statistics show that for the first time ever, the average price of a new vehicle has climbed beyond $50,000, marking a significant shift in consumer spending habits.
This upward trend coincides wiht persistently high delinquency rates on auto loans among borrowers with suboptimal credit scores.Wealthier individuals are actively acquiring new vehicles, whereas budget-conscious shoppers frequently enough postpone purchases or turn to used cars as more economical alternatives.
Financial Inequality Shapes Automotive Purchasing Patterns
The car market today is largely driven by households with robust financial standing and access to favorable loan terms. These consumers sustain demand at premium price points, effectively pushing those with limited budgets toward less costly options or delaying acquisition altogether.
The concept of a “K-shaped” economic recovery remains highly relevant: one segment experiences growth and prosperity while another grapples with inflationary pressures and stagnant wages. Such as, rising equity in real estate and booming investment portfolios have enhanced wealthier Americans’ ability to spend-contrasting sharply against middle- and lower-income groups facing escalating living expenses without corresponding income gains.
Subprime Borrowers Face Increasing auto Loan Difficulties
Individuals classified as subprime borrowers-those holding FICO scores below 620-are encountering mounting challenges amid climbing interest rates on auto financing. Current averages place loan rates near 9%, but subprime customers frequently face double-digit APRs ranging from 18% to 20%, substantially raising their risk of default.
This dynamic has contributed to elevated delinquency levels; recent data indicates that over 6% of subprime auto loans were at least two months past due-a figure approaching historic highs. Conversely, borrowers with stronger credit profiles have maintained relatively stable repayment patterns despite ongoing economic uncertainties.
Auto Financing Struggles Reflect broader Household Budget Pressures
Total outstanding U.S. auto debt now surpasses $1.7 trillion, highlighting widespread dependence on vehicle financing amid soaring prices nationwide. Complaints related to auto loans have surged sharply in recent years as affordability concerns intensify alongside complex loan terms.
A notable rise in monthly payments exceeding $1,000 has been observed; nearly one-fifth of all financed new-car purchases fall into this category-a level nearing previous record highs from earlier quarters. This escalation places additional strain on household finances already stretched thin by inflation affecting essentials such as housing and food costs.
The Impact of Electric Vehicles on Average Purchase Prices
A major contributor behind record-high transaction prices is surging demand for electric vehicles (EVs), which generally command higher price tags than traditional gasoline-powered models. The average sale price for a new EV recently surpassed $58,000 as buyers rushed before federal tax credits worth up to $7,500 expired at September’s end.
This surge illustrates how government incentives can temporarily boost sales but also contribute to overall market inflation when combined with global supply chain disruptions and tariff-driven manufacturing cost increases.
An industry at a Crossroads Amid Affordability Challenges
The current environment presents both opportunities and risks: luxury EV sales soar among affluent consumers fueling record revenues for automakers like Tesla and General Motors’ electric divisions; meanwhile affordability remains elusive for many Americans reliant on credit under challenging conditions.
“The automotive sector today starkly reflects broader economic realities,” said an industry analyst focused on consumer trends. “With prices breaking historic records driven largely by wealthy households investing heavily in electric vehicles-and others pushed toward used markets-the stage is set for profound disruption.”
Future Outlook: Implications for Consumers & The Economy
- Divergent Consumer experiences: Wealthy individuals benefit from asset thankfulness enabling sustained spending power; lower-income groups face tightening budgets worsened by high borrowing costs;
- Lending Sector Risks: Rising delinquencies among subprime borrowers highlight potential vulnerabilities within financial institutions dependent on auto loan portfolios;
- Sustainability Questions: Heavy reliance on government subsidies raises concerns about long-term stability once incentives phase out;
- Pursuit Of Equitable Innovation: Automakers must balance electrification ambitions while ensuring accessibility across diverse income levels;
A Practical Illustration: Urban Professionals vs Rural Buyers
An illustrative contrast emerges between urban professionals benefiting from remote work versatility who frequently enough opt eagerly for pricier EV models supported by employer programs or tax breaks-and rural residents who rely heavily on dependable used vehicles due primarily to affordability constraints despite longer commutes requiring reliable transportation solutions alike.