China Implements Ban on Nvidia AI Chips, Altering the Global Technology Arena
Chinese Authorities Prohibit Domestic Firms from Procuring Nvidia AI Hardware
The Cyberspace administration of China (CAC), responsible for overseeing internet regulations nationwide, has officially barred local technology companies from purchasing Nvidia’s AI chips. This decisive policy shift signals a new phase in China’s stance toward foreign semiconductor technologies and directly affects industry leaders such as bytedance and Alibaba.
Consequences for Leading chinese Tech Corporations and Market Shifts
The government mandate specifically orders firms to halt testing and procurement of the Nvidia RTX pro 6000D server chip, a model customized for the Chinese market. This action builds upon previous initiatives encouraging reliance on domestic semiconductor solutions rather than imported ones. Given that companies like Huawei are advancing their own AI processors but Nvidia remains the global frontrunner with some of the most advanced chipsets available, this ban is poised to significantly disrupt China’s technology ecosystem.
Escalating US-China Semiconductor Rivalry
This growth unfolds amid intensifying geopolitical tensions over semiconductor trade. Earlier US policies imposed stringent licensing restrictions on American chip manufacturers-including Nvidia-curtailing their ability to export cutting-edge AI chips to China. These constraints reportedly led to an $8 billion revenue loss for Nvidia in a single quarter during 2023.
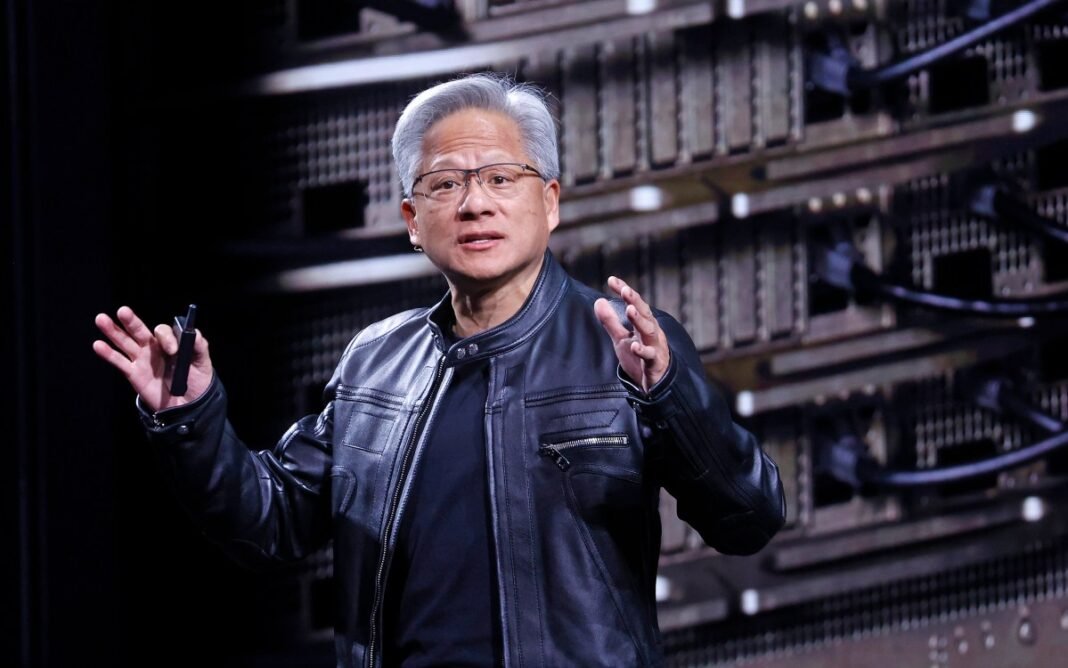
Nvidia’s Strategic Position Amid Regulatory Obstacles
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang conveyed cautious disappointment while recognizing the complex political environment between China and the United States: “We can only serve markets where we are welcome,” he remarked at a recent conference. Huang stressed patience and reaffirmed support for Chinese clients within permissible regulatory frameworks.
Evolving Trade Regulations and Their Ripple Effects
earlier in 2024, following initial US-imposed restrictions under prior administrations, there was a temporary easing allowing semiconductor sales into China under strict conditions-such as revenue-sharing agreements requiring up to 15% of proceeds be returned to US authorities. Despite these concessions announced mid-year, actual transactions under this arrangement have been limited due to slow bureaucratic processes.
Global Implications for Artificial intelligence Chip Markets
- Pursuit of Self-Sufficiency: In response to these limitations, Chinese enterprises are rapidly increasing investments in indigenous chip design efforts aimed at reducing dependency amid ongoing supply chain uncertainties.
- Sustained Market Dominance: While emerging competitors like South Korea’s Samsung and Taiwan’s TSMC gain ground globally, Nvidia continues commanding a dominant share of high-performance AI accelerator sales worldwide.
- The Geopolitical Battleground: Semiconductors remain central in international power struggles as nations compete thru innovation incentives alongside trade restrictions seeking technological supremacy.
A Comparable Shift: Lessons from Smartphone Manufacturing realignments
This situation echoes past transformations witnessed when smartphone component exports faced tariffs or controls; manufacturers swiftly diversified suppliers or localized production capabilities.Similarly, China’s intensified focus on homegrown chip development reflects strategic adaptations seen across other advanced tech sectors confronting geopolitical challenges today.
Navigating Future Challenges in Semiconductor Commerce
The intersection between national security priorities and commercial interests ensures that semiconductor trade policies will continue evolving throughout 2025 and beyond. Companies like Nvidia must carefully balance adherence to shifting regulations while striving to maintain leadership in innovation despite restricted access to critical markets such as China-the world’s second-largest economy with GDP surpassing $18 trillion as of mid-2024.
“Success for global technology enterprises depends not only on superior products but also mastering complex international policy environments.”
This dynamic landscape highlights how deeply intertwined technological advancement has become with diplomatic strategy-a reality influencing investment choices across Silicon Valley hubs and Beijing alike.