Leadership Transitions Amid NASA’s Budgetary Challenges
The recent proposal to reduce NASA’s funding by 25 percent has sparked a notable wave of resignations within the agency, including the departure of Makenzie Lystrup. Serving as director of the Goddard Space Flight Center as April 2023,Lystrup announced her resignation effective August 1.
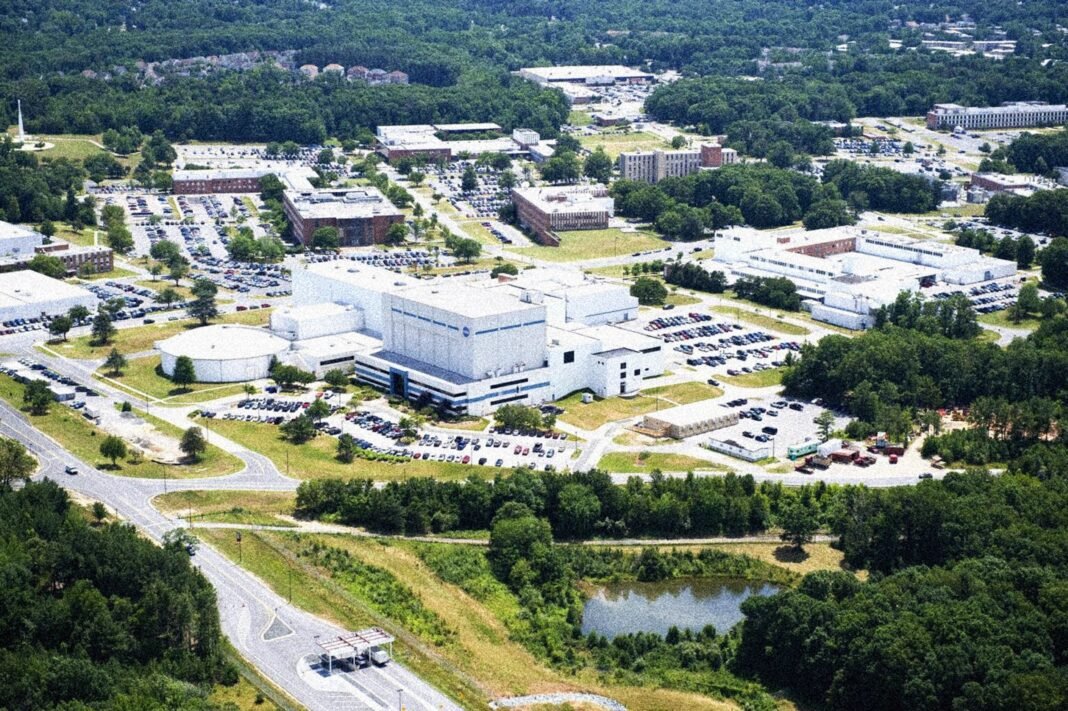
Goddard Space Flight Center: A Cornerstone for Scientific Innovation
Under lystrup’s leadership, Goddard managed a workforce exceeding 8,000 employees and operated with an annual budget close to $4.7 billion in the last fiscal year. As NASA’s largest field center focused on scientific research and robotic mission development, Goddard rivals human spaceflight centers located in Florida, Texas, and Alabama in both scale and impact.
This center is instrumental in overseeing major projects such as the James Webb Space Telescope and Hubble Space Telescope currently orbiting Earth. Additionally, its teams are assembling the Nancy grace Roman Space Telescope-an advanced observatory set for launch next year that aims to deepen our understanding of dark energy and exoplanets.
Expanding Reach Through Multiple facilities
Goddard also manages several satellite facilities including Wallops Flight Facility (virginia), Katherine Johnson Independent Verification & Validation Facility (West Virginia), White Sands Complex (New Mexico), and Columbia Scientific Balloon Facility (Texas). Approximately 60 percent of its funding originates from NASA’s Science Mission Directorate accounts supporting astrophysics, Earth science, heliophysics, and planetary science initiatives.
A New Era at Goddard Leadership
Cynthia Simmons will step into the role of acting director following lystrup’s exit. With over 25 years at Goddard starting as a contract engineer before ascending through various leadership positions, Simmons brings deep institutional knowledge to guide the center during this transitional period.
Before her tenure at NASA leadership levels, Lystrup made significant contributions at Ball Aerospace-now part of BAE Systems-where she led civilian space programs for federal agencies including NASA. Her academic credentials include a PhD in astrophysics from University College London with specialized research experience in planetary astronomy.
The Impact of Proposed Budget Reductions on Core Missions
The fiscal year 2026 budget request proposes $18.8 billion for NASA-a sharp decline from nearly $25 billion allocated this year-and cuts funding for its Science Directorate by almost half ($7.3 billion down to $3.9 billion).These drastic reductions threaten cancellation or severe downsizing across numerous ongoing or planned missions spanning multiple scientific disciplines within NASA’s portfolio.
This financial strain disproportionately affects centers like Goddard that rely heavily on these funds to sustain cutting-edge scientific projects recognized globally by researchers across continents.
Legislative Pushback & Potential Constitutional Disputes
- Recent appropriations committee bills seek to restore funding near current levels; however they must still pass full congressional approval before presidential endorsement can occur.
- Tensions persist due to executive branch attempts via impoundment-the refusal to spend congressionally approved funds-to enforce deeper cuts irrespective of legislative decisions; this raises constitutional questions about separation-of-powers between Congress and Executive Branch concerning federal budgets.
An Internal Call for Strategic Program Management
“Major programmatic changes within NASA require careful strategic implementation so risks are minimized,” states an open letter signed by hundreds of current and former employees known as “The voyager Declaration.” The letter criticizes recent policy shifts viewed as wasteful or harmful toward public resource management while jeopardizing safety standards along with national security interests.
“We strongly urge against enacting damaging cuts proposed by this management,” it emphasizes “as they undermine essential scientific progress necessary for fulfilling Congress-mandated missions.”
A Broader Pattern Among Federal Agencies’ Workforce Protests
This declaration mirrors similar employee-led resistance recently observed at institutions such as NIH and EPA where staff opposed abrupt policy reversals threatening core operational goals driven more by political agendas than evidence-based planning principles.
The Wider Consequences Across Key Centers Beyond Goddard
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena faces comparable challenges amid these budget uncertainties. JPL oversees many robotic exploration programs including Mars rover missions alongside upcoming launches like Europa Clipper targeting Jupiter’s icy moon expected later this decade.
Earlier this summer JPL Director Laurie Leshin resigned after managing layoffs exceeding ten percent last year amidst doubts surrounding flagship projects such as Mars Sample Return-which may be canceled under current proposals favoring future crewed expeditions instead.
This shift signals a potential pivot away from robotic precursors toward human exploration despite decades-long technological advancements enabled largely through autonomous spacecraft development led out west at JPL alongside East coast efforts centered around facilities like Goddard.
Navigating Fiscal Constraints While Safeguarding Innovation’s Future
The convergence of leadership changes combined with looming financial pressures places immense strain on sustaining momentum within America’s leading space agency during an era marked both by groundbreaking discoveries yet unprecedented political challenges.NASA continues serving not only as a beacon scientifically but symbolically-as an inspiration driving generations worldwide toward exploring beyond our planet-and protecting its mission demands prudent stewardship amid evolving governmental priorities now more than ever before.