Challenges Facing TeslaS Robotaxi Rollout in california
Overview of tesla’s Autonomous Ride Trials
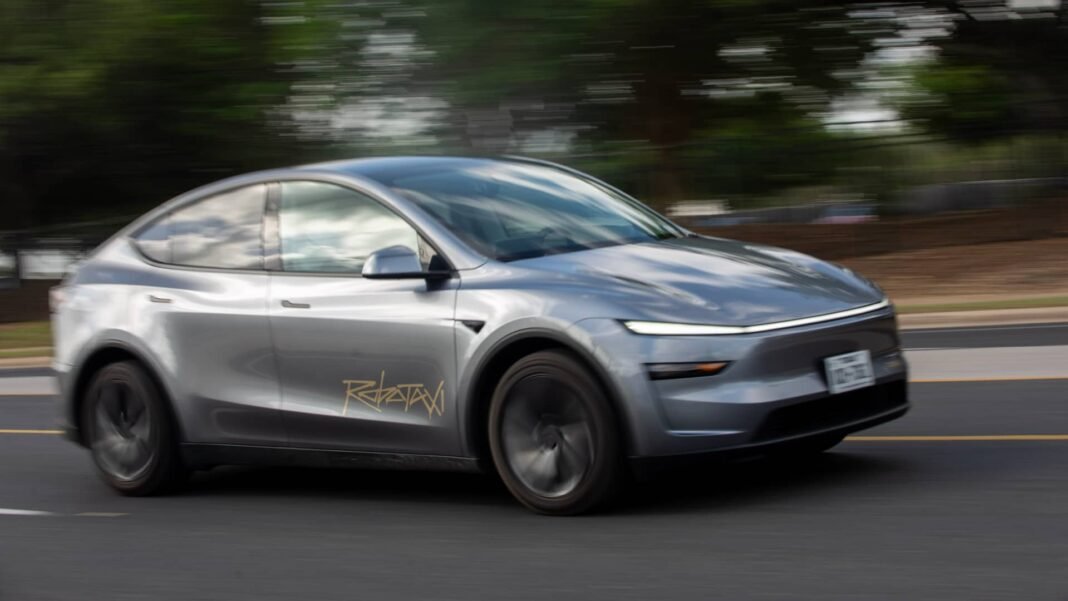
Tesla is currently conducting a pilot robotaxi program in Austin, Texas, utilizing Model Y SUVs outfitted with the company’s cutting-edge autonomous driving software. This limited service operates exclusively during daylight hours and favorable weather conditions on roads where speed limits do not exceed 40 mph. Each trip includes a human safety driver seated inside the vehicle while Tesla staff remotely oversee operations. Participation is restricted to select individuals invited through Tesla’s early access initiative.
Plans for Expansion Amid Regulatory Barriers
The automaker has announced intentions to extend its robotaxi services into the San Francisco Bay Area and other parts of the United States. However, this expansion faces meaningful regulatory challenges that prevent fully driverless rides on public streets within California at present.
California’s Strict Rules on Autonomous Passenger Transport
the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) mandates that any autonomous vehicle transporting passengers-whether paying or not-must have a human operator physically present behind the wheel at all times. Under these regulations, Tesla cannot offer driverless ride-hailing services legally within state boundaries.
Tesla holds a charter-party carrier license in California permitting it to operate private car services akin to limousine or tour companies but strictly with human drivers rather than automated systems.Recently, Tesla informed CPUC about plans to expand its permitted non-autonomous operations across much of the Bay Area for employees’ friends and family as well as select public users.
Drivered Testing Permits vs Commercial Deployment
The California Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) has granted Tesla a “drivered testing permit” as 2014, allowing autonomous vehicle trials only when an employee or contractor designated by Tesla occupies the driver seat as a safety monitor. This permit explicitly forbids charging customers for rides during such tests.
Concerns Over Marketing Practices and Safety Claims
The DMV has expressed apprehension regarding how Tesla promotes its advanced driver assistance technologies-previously known as Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD). Although official documentation stresses that drivers must remain attentive with hands on the wheel at all times, social media videos reveal some users engaging FSD without supervision while performing unrelated tasks behind the wheel.
This inconsistency has prompted regulators to question whether Tesla should retain authorization to sell vehicles equipped with these features in California amid ongoing consumer protection hearings focused on potential misrepresentation risks associated with semi-autonomous driving systems.
Community Feedback and Transparency Challenges
Local officials from Marin County voiced surprise over being uninformed about possible robotaxi deployments within their jurisdictions. Several supervisors emphasized that open interaction from companies like Tesla would improve community trust ahead of disruptive technological introductions affecting local transportation networks.
“I certainly expect they will tell us, and I think it’s good business practice,” remarked one county board member reflecting mixed sentiments toward emerging robotaxi services impacting regional transit dynamics.
A Comparative Look: Waymo’s Regulatory Success Story
Waymo, owned by Alphabet Inc., stands out as an industry leader having secured regulatory approvals enabling fully driverless ride-hailing operations across parts of California as 2023 under CPUC permits allowing commercial use without onboard safety drivers. The company continues expanding coverage through amendments granted by both DMV and CPUC authorities while also conducting supervised testing in cities like New york City and Philadelphia where it is scaling up service areas rapidly.
Navigating Future Prospects for Autonomous Ride Services
Tesla’s ambitions underscore both remarkable technological strides toward mainstream robotaxis alongside intricate legal frameworks shaping their deployment across various states today. While pilot programs showcase promising advancements in autonomous mobility technology, widespread commercial adoption hinges upon overcoming evolving regulations primarily designed around passenger safety concerns amid rapid innovation cycles within bright transportation sectors worldwide.





