Breakthroughs in Lyme Disease Prevention: A New Dawn
Rising Incidence of Lyme Disease Across Regions
Lyme disease, a bacterial infection transmitted through tick bites, has surged as a significant health challenge throughout North America and parts of Europe. Recent data reveal that Canada has recorded over 35,000 confirmed cases since 2010, with numbers climbing sharply due to the expanding habitats of ticks. In the United states alone, more than 120,000 cases were reported in 2023 by health authorities; however, experts believe actual infections could be up to five times higher because manny remain undiagnosed or unreported.
The Ecology and Behavior of Ticks Driving Infection Rates
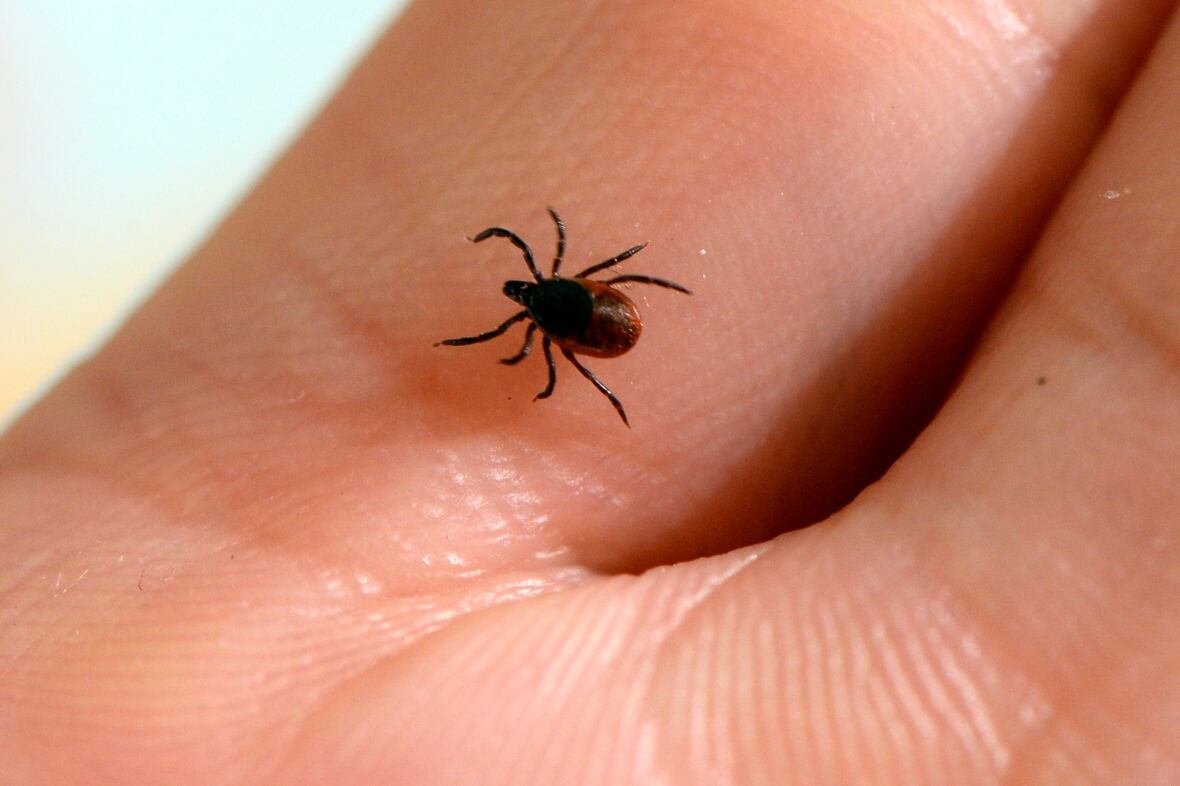
The blacklegged tick (Ixodes scapularis) is the primary vector responsible for transmitting Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium causing Lyme disease. These tiny arachnids flourish in forested environments and tall vegetation where they attach themselves to humans or animals for blood meals. While not every tick carries this pathogen, those infected can transmit it if attached for at least 24 hours.
Expanding Tick Territories and Their impact on Communities
First identified near Lake Erie in Ontario during the late 1970s, blacklegged ticks have now spread across seven Canadian provinces. Nova Scotia reports some of the densest populations not only in rural woodlands but increasingly within urban parks and green spaces-raising concerns about exposure even within city limits.
A promising Vaccine candidate Enters Advanced Trials
A novel vaccine developed collaboratively by Pfizer and Valneva SE is currently undergoing Phase 3 clinical trials expected to conclude by December this year. This vaccine prompts the immune system to generate antibodies targeting a specific protein on Borrelia burgdorferi. when vaccinated individuals are bitten by infected ticks,their immune response can neutralize bacteria before symptoms develop.
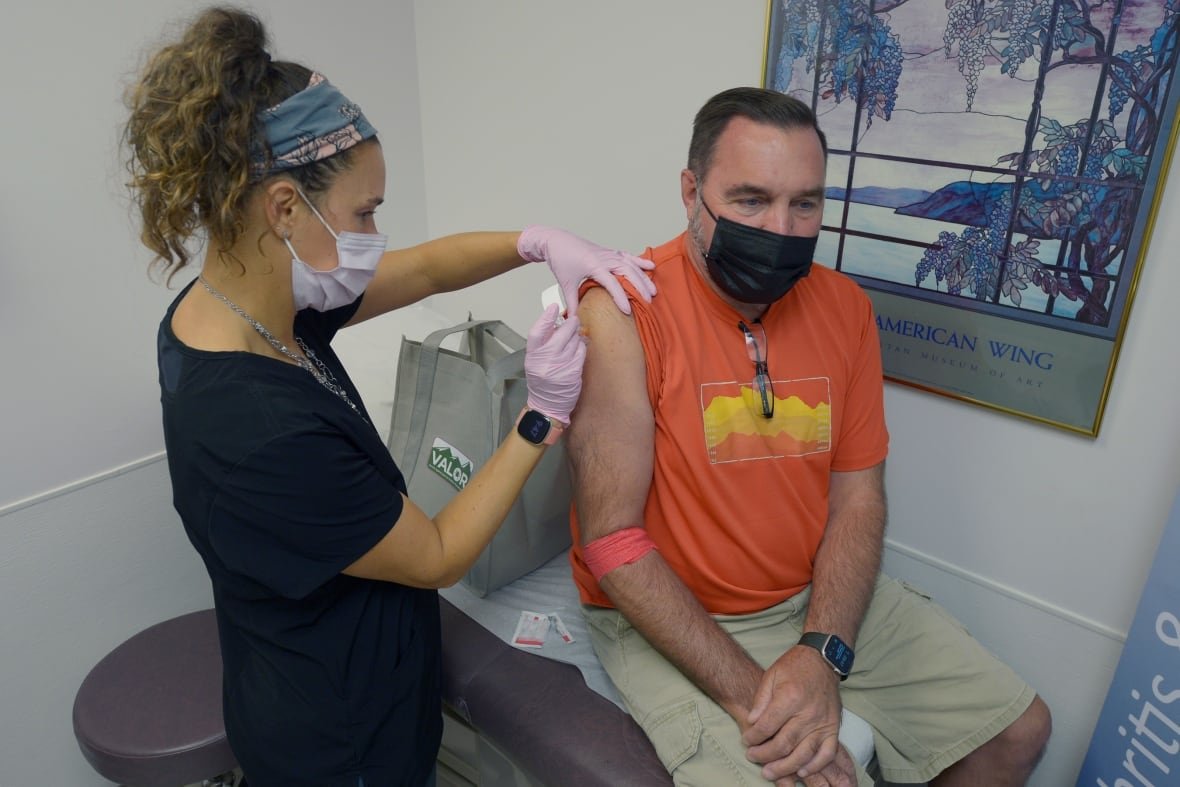
If trial outcomes remain positive, pfizer plans to seek regulatory approval from agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Governance (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) by late 2026; timelines for Health Canada submissions are yet undetermined.
Target Groups Enrolled in Clinical Studies
The research focuses on individuals frequently exposed to tick habitats: landscapers working outdoors daily; avid hikers exploring wooded trails; gardeners spending extended time outside; pet owners whose dogs often return with attached ticks-all facing heightened risk of infection.
The Historical Context: Lessons from past Vaccines
An earlier human vaccine against Lyme disease was available between 1998 and 2002 but was withdrawn due mainly to low demand combined with public apprehension about side effects despite no definitive evidence linking it to adverse outcomes. This setback delayed progress until renewed scientific interest emerged amid rising global case counts over recent years.
“Previous controversies slowed advancement efforts substantially; however current candidates demonstrate substantial potential,” note microbiologists involved indirectly with ongoing research initiatives.
Choice Strategies Beyond Direct Human Immunization
- Mice-targeted oral vaccines: Researchers at institutions like University of Tennessee Health Science Center have created edible bait pellets designed to immunize wild mice populations-the main reservoirs harboring Borrelia burgdorferi. by lowering bacterial prevalence among these rodents-the source infecting larval ticks-local transmission risk may drop dramatically (studies indicate reductions up to approximately 75%).
- Tackling tick feeding mechanisms: Experimental vaccines aimed at preventing successful blood feeding by ticks could offer protection against multiple tick-borne diseases simultaneously-a promising frontier still under investigation.

Lived Realities Emphasize Urgency for Effective Solutions
Diana Moser from East LaHave wears insect-repellant treated clothing while gardening but remains hopeful that vaccination will provide stronger protection against this elusive illness affecting several acquaintances-including one who endured repeated infections leading to chronic joint pain alongside neurological complications severely impacting daily life quality.
“Lyme disease is unpredictable,” she shares thoughtfully. “It attacks deeply-causing relentless joint inflammation plus nervous system issues.”

The Critical Role Of Vaccination For Outdoor Workers And Enthusiasts
< p >Colin chase , an enthusiastic forest explorer volunteering as search-and-rescue personnel navigating dense Nova Scotia woods , describes how despite careful precautions-including thorough self-examinations after outings , washing clothes immediatly -ticks sometimes evade detection . He welcomes any safe , effective vaccination option :“Without protective measures like vaccination , people might avoid nature altogether . But there’s so much natural beauty worth preserving.”
< h2 >Future Directions: Combining Multiple Approaches To Fight Lyme Disease
< p >Experts agree that no single intervention will suffice against such a complex vector-borne illness . Integrating personal protective behaviors ; environmental management tools such as mouse vaccination stations placed near homes or recreational areas ; along with widespread availability of effective human vaccines could substantially reduce incidence rates over time . Collaborative efforts between governments and private sectors aim toward regionally tailored programs based on local ecological conditions .
< figure >< img loading = "lazy" alt = "Dog sitting amidst tall grass outdoors." src = "https://newsfeed24.website/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/localimages/dog-long-grass-lyme-disease.jpeg" >
< figcaption >Pets frequently bring home unwelcome hitchhikers like infected ticks posing risks inside households.(Brian MacKay/CBC)





